Building Blocks for AI: Unpacking the Essentials of Training Data for Computer Vision in Digital Pathology (P.1)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative domain in digital pathology. The task of training computer vision (CV) models, however, presents unique challenges. The quality and quantity of training data significantly influence model performance.
 Overview (Image created by the author)
Overview (Image created by the author)
In this succinct review, I distill the key characteristics of effective training data, drawing on my empirical observations.
Image Quality
The quality of histopathological whole slide images (WSIs) is crucial. High-resolution images allow the model to detect subtle patterns and features that may be indicative of disease. A minimal number of tissue-process artifacts also contributes to the high quality of WSIs.
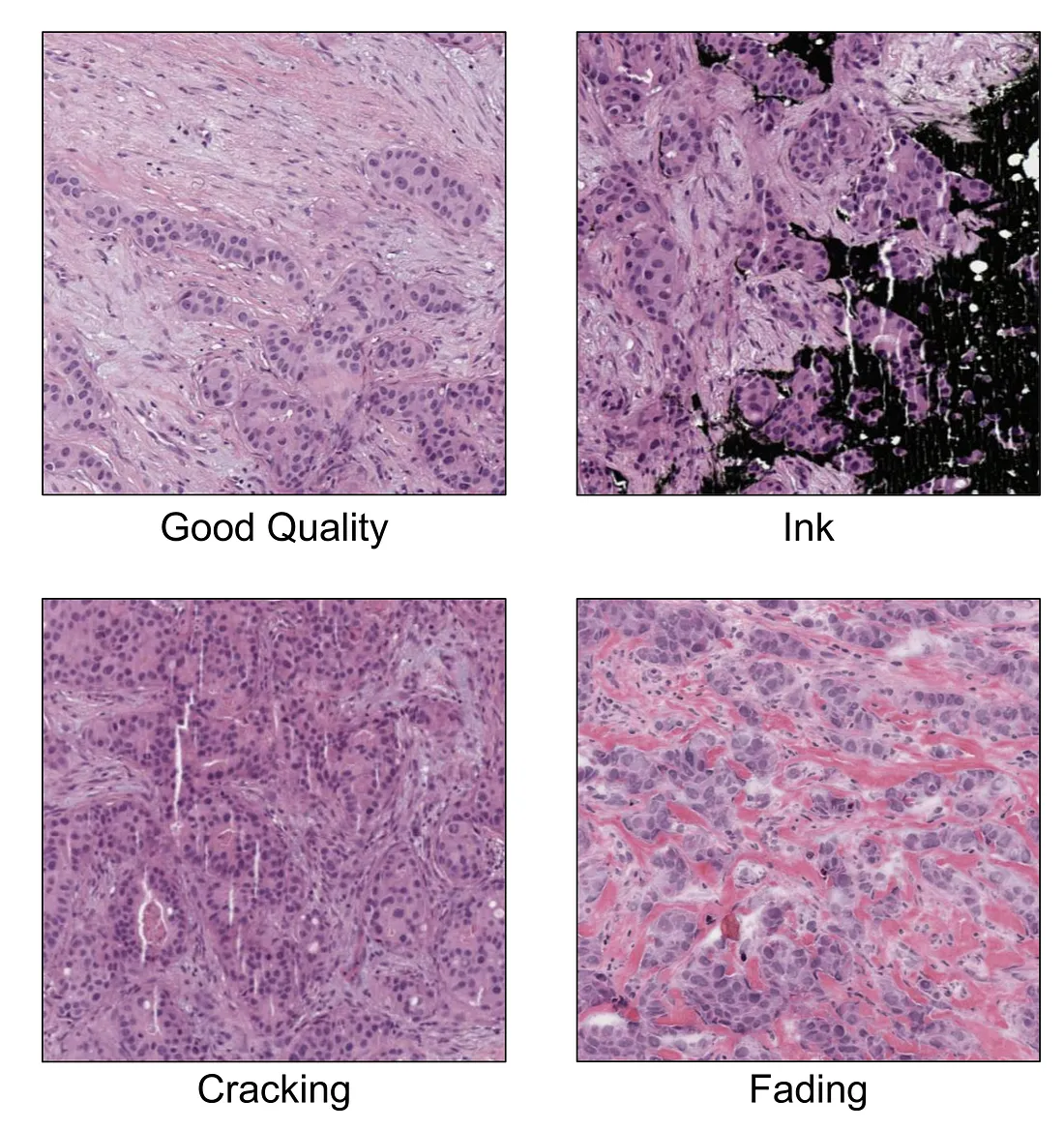 Variation of Image Quality (Image created by the author)
Variation of Image Quality (Image created by the author)
Proper Annotation
Images should be annotated by experts in the field. These annotations serve as labels for the training data and guide the model in learning the task. Therefore, bad annotations lead to bad labels, which, in turn, dampen the model’s performance and reliability. I also have a blog on how to decide the strategy of annotation [1], please take a look.
Representative
The dataset should include images representing a variety of conditions and stages of disease. This helps the model learn to recognize a wide range of scenarios. It is noteworthy that the diversity of morphological features requires a more complex model architecture and, therefore, larger samples. Therefore, one should find the balance between the diversity of data, the complexity of the CV model, and the sample size.
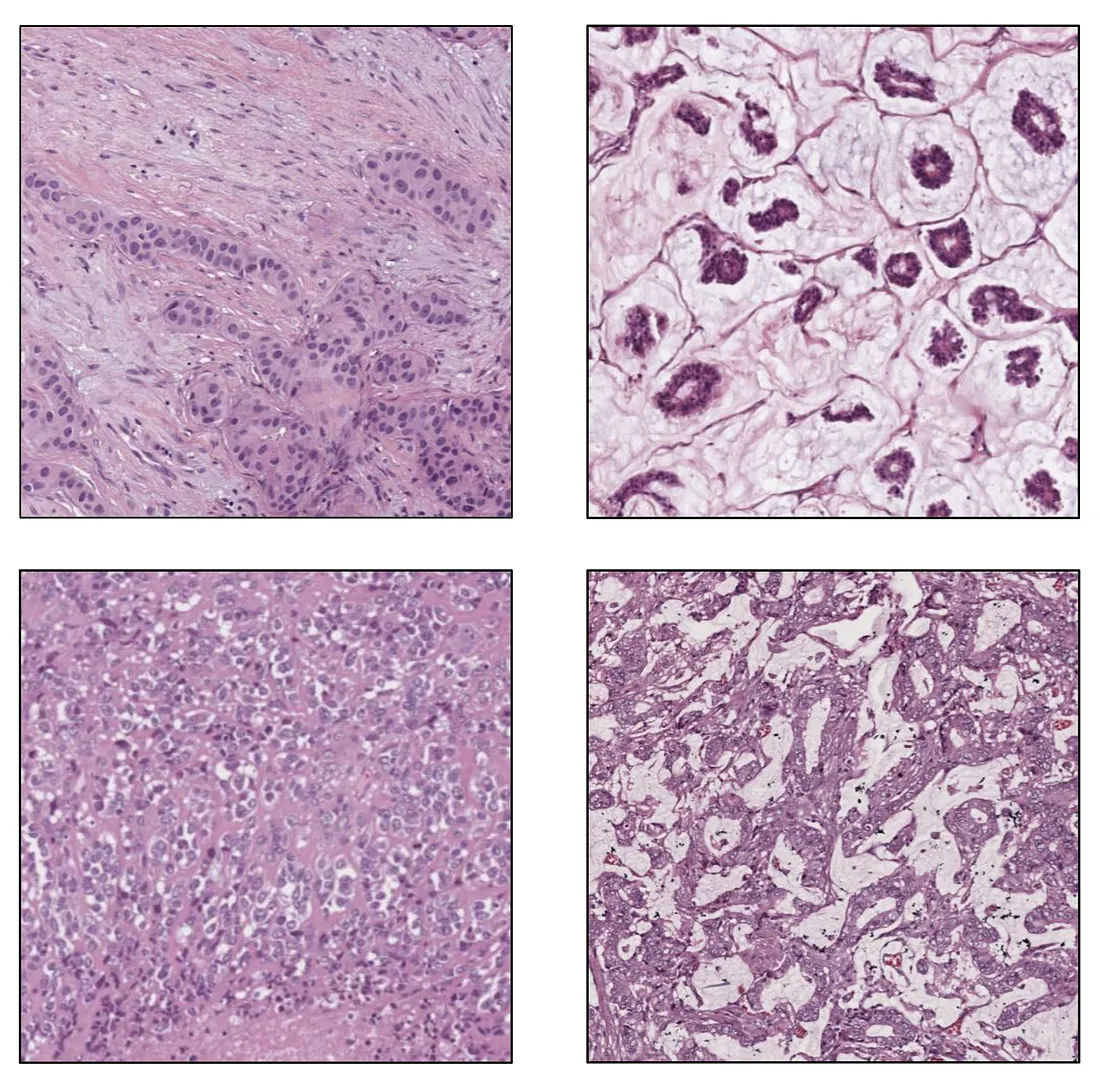 Variation in Histologic Variant (Image created by the author)
Variation in Histologic Variant (Image created by the author)
Staining Consistency
Histopathological images are often stained to highlight certain features. The staining process should be consistent across all images, as variations can affect the model’s performance. In reality, staining protocols exhibit intra-technician, inter-technician, and inter-institutional variability. It is an inevitable issue, which can only be minimized by careful study designs.
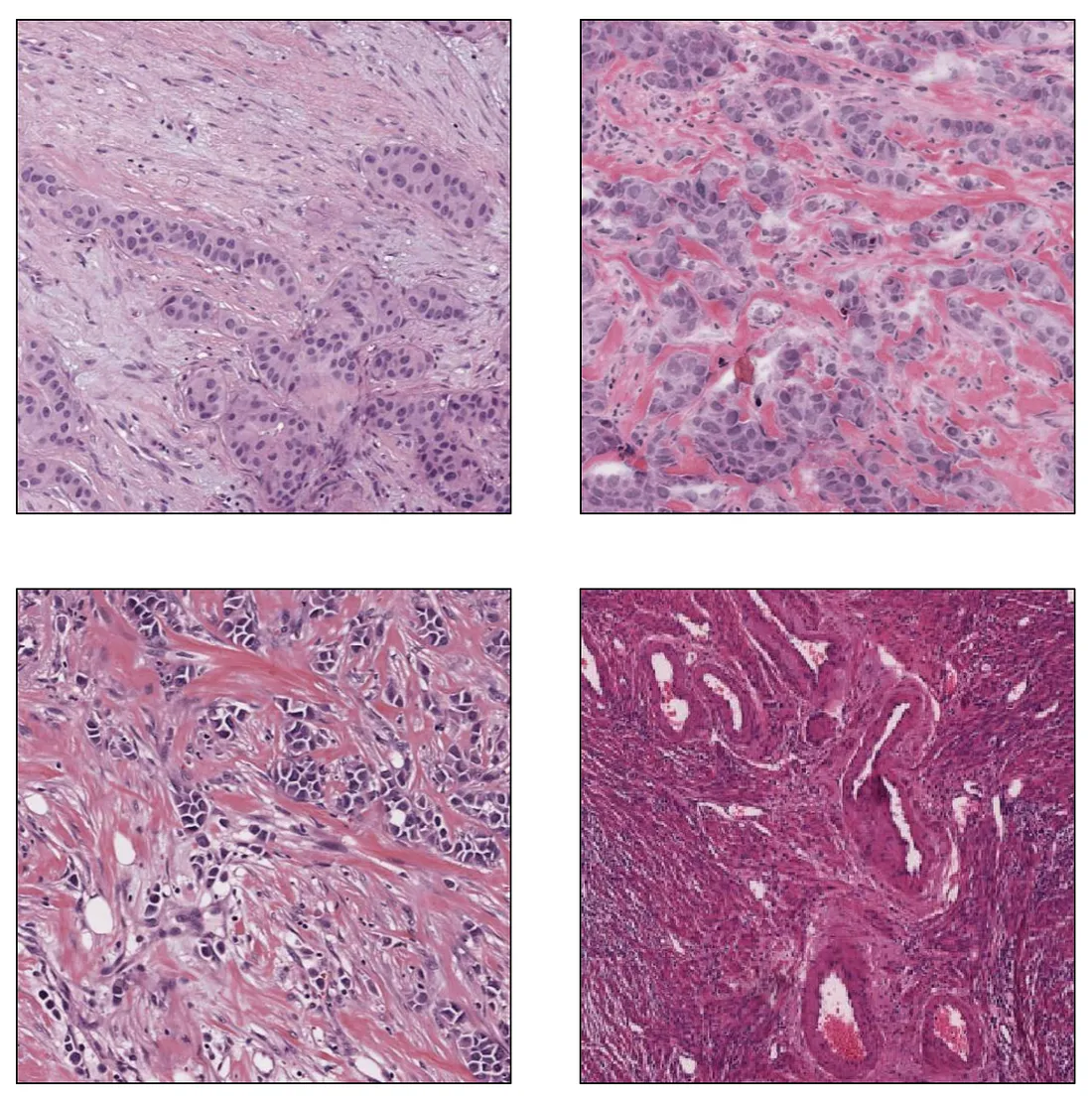 Staining Inconsistency (Image created by the author)
Staining Inconsistency (Image created by the author)
Balanced Classes
It is also important to ensure that classes of interest are balanced if a classification task is performed. Having too many examples of one class and not enough of another (Imbalance Learning) can lead the model to become biased. Careful study designs are important to balance the classes of interest.
Conclusion
Making sure the quality of train data is one of the most important steps toward building AI models in digital pathology. In addition to training data, paying attention to how to compile test data is also vital to correctly evaluating these models [2].
To those who may be interested, I hope you enjoy this mini-review.
References
- Minh-Khang Le. “Embarking on a Journey: A Novice’s Guide to Histopathology Annotation in Deep Learning.” Medium, 1 Dec. 2023, medium.com/@minhkhangle.phd/embarking-on-a-journey-a-novices-guide-to-histopathology-annotation-in-deep-learning-b664ecbec24c.
- Homeyer, André, et al. “Recommendations on Compiling Test Datasets for Evaluating Artificial Intelligence Solutions in Pathology.” Modern Pathology, vol. 35, no. 12, 1 Dec. 2022, pp. 1759–1769.